Negative Binomial Distribution
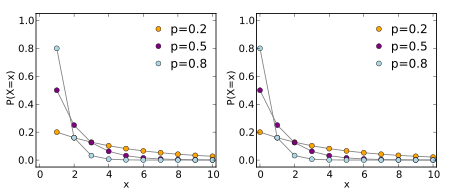
a) Notation X ∼ NegBin(r, p)
b) Interpretation Negative Binomial Distribution describes the number of failures before the rth success in Bernoulli trials with probability p of success and probability of 1 - p of failure on each trial.
c) Type: Discrete
d) Parameter(s): r - the rth success, the stopping parameter p - the probability of success on each trial
e) Probability Density Function:
f) Range: r[0, ∞) p[0, 1] x[0, r]
g) Mean:
h) Variance:
i) Application:
Generally, Negative binomial is a generalized case of binomial distribution and geometric distribution. Binomial distribution can only simulate the probability distribution when the number of success is 1 and geometric distribution can only find the probability of the time the first success occurs while negative binomial can estimate the probability distribution. The following are some real world examples where regular negative binomial distribution can be used.
An oil company shows that an exploratory oil well should have a 0.2 chance of striking oil. The probability that the first strike comes on the third well drilled. For coin tosses, the probability that we have the third heads on the 10th trial.
The inverse binomial sampling, a derived technique from negative binomial is useful in sampling biological populations. If the proportion of individual items possessing a certain characteristic is p and we sample individuals from population until we see r such individuals, then the number of individuals sampled can be estimated and follows the negative binomial distribution