Beta Distribution
- Notation
- Interpretation
- Beta distribution is a very versatile way to represent probability of outcomes since it is defined on the continuum between 0 and 1. Beta distribution can describe our subjective degree of belief in Bayesian sense. When , is equivalent to .
- Type:
- Continuous
- Parameter(s):
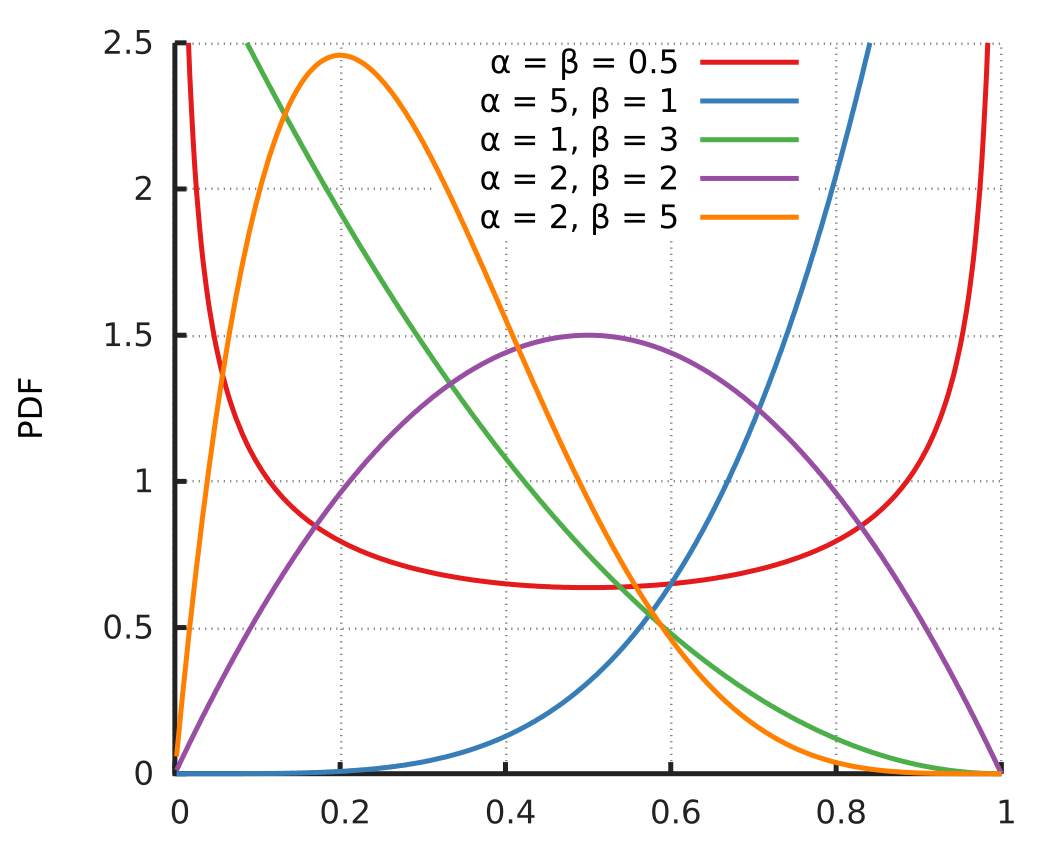
- - the shape parameters of beta distribution.
- Probability Density Function:
- Range:
- Mean:
- Variance:
Application:
Beta distribution can represent a distribution of all possible values of probabilities when the actual distribution is unknown to us. Thus, beta distribution is often used as prior probability distribution in Bayesian inference to indicate our initial assumption about the actual distribution.
For example, we want to estimate the probability that a basketball player hits a free-throw, given that we watch him attempt 100 of them. Before we have seen him throw, we have justified assumptions that he almost certainly cannot shoot more that 95% free throws and can hopefully hit the shot at least some of the time. We represent our prior knowledge in a Beta distribution called the prior. Next, we observe 100 free-throws and see that 80 are good. Then by modeling these actions with a beta-binomial distribution, we can now update our knowledge of the true probability distribution of the basketball player hits a free-throw.
This is represented as a Beta distribution itself called the posterior distribution. How beta distribution, prior and posterior distribution are used in bayesian statistics will be introduced later in here.