Exponential Distribution
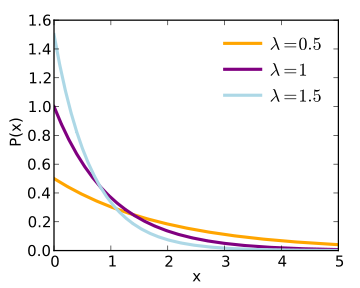
- Notation
- Interpretation
- Exponential distribution, a continuous analogous of poisson distribution, can be used to describe the waiting time until the first event occurs when the happening rate of the event is very large.
- Type:
- Continuous
- Parameter(s):
- - the rate of event, which measures the number of event occur per unit time
- Probability Density Function:
- Range:
- Mean:
- Variance:
Application:
- Exponential distribution is very useful because of its memoryless property. For example, in the case of atom decaying, given survival to time , the chance of surviving to time in the future is not affected.
- In science, exponential distribution is often used to simulating the half life decaying of atom. For example, suppose we know the average lifetime of a particular atom and its lifetime is approximately exponentially distributed, we can use exponential distribution to estimate the probability that this particular atom is not decayed after a fixed amount of time.
- Also, since exponential distribution is the continuous analogue of poisson distribution, continued from the customer arriving example from poisson distribution, exponential distribution can also help us to know more information about the arriving time of customers, the likelihood of having customers arrived within a time interval. For example,
- The probability that no customer arrives between the first three units of times.
- The probability that the first customer arrives after a certain time takes more than 2 units of time.
- The probability that the 4thcustomer arrives within 1 unit of time of the arrival of the previous customer.
- The probability that the 1thcustomer arrive takes less than 0.5 units of time and the waiting time between and customers is more than 4 units of time.