What is A-search?
A-search is a graph search algorithm that evaluates nodes by a function f(n), which combines a new term, g(n), or the cost to reach the node, and h(n), the cost to get from the node to the goal:
Since is the path cost from the current node n to a potential successor m, and is the estimated cost of the cheapest path from a node n to the goal, we have: = estimated cost of the cheapest solution through n.
Now, let’s use the previous example to see how A-search works. Below is a map that we are going to search the path on.

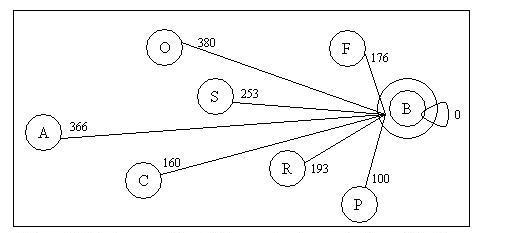
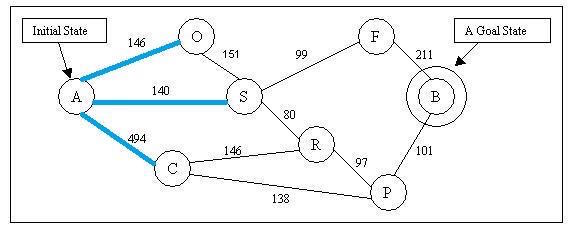
According to the estimate function f(n): Node O’s f(n) = g(A,O) + h(O) 146+380 = 526, Node S’ f(n) = g(A,S) + h(S) = 140 + 253 = 193, Node C’s f(n) = g(A,C) + h(C) = 494 + 160 = 654. The algorithm will choose to explore node S. After explored S, we have new node R and F reachable now.
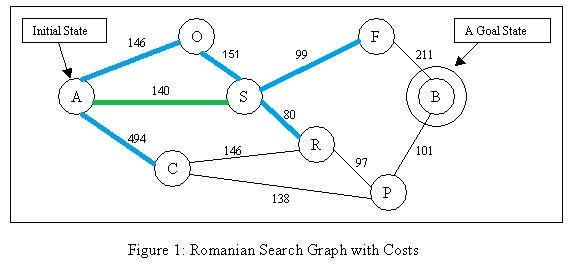
According to the estimate function f(n): Node O’s f(n) = 526, Node C’s f(n) = 654, Node F’s f(n) = 239 + 176 = 415, Node R’s f(n) = 220 + 193 = 413. The algorithm will choose to explore node R. After explored R, we have new node P reachable now.
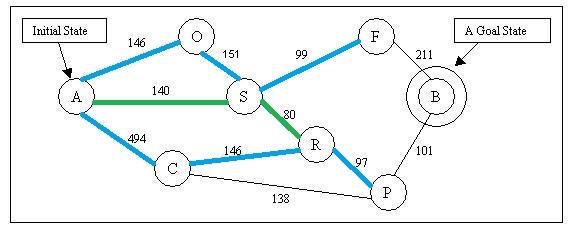
According to the estimate function f(n): Node C’s f(n) = 413 + 146 + 160= 719 Node P’s f(n) = 413 + 97 + 100 = 610. The algorithm will choose to explore node P. After explored P, we have new node B reachable now, which is our goal node.
